Study identifies target for disease hyper progression after immunotherapy in kidney cancer
Researchers find that cancer cells mimic myeloid cells to hide from the immune system and promote disease hyper progression after immunotherapy
Inhibiting the myeloid mimicry pathway along with immunotherapy improves antitumor outcomes in preclinical models
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have found that renal medullary carcinoma (RMC) cells use an adaptive mechanism called “myeloid mimicry” to hide...
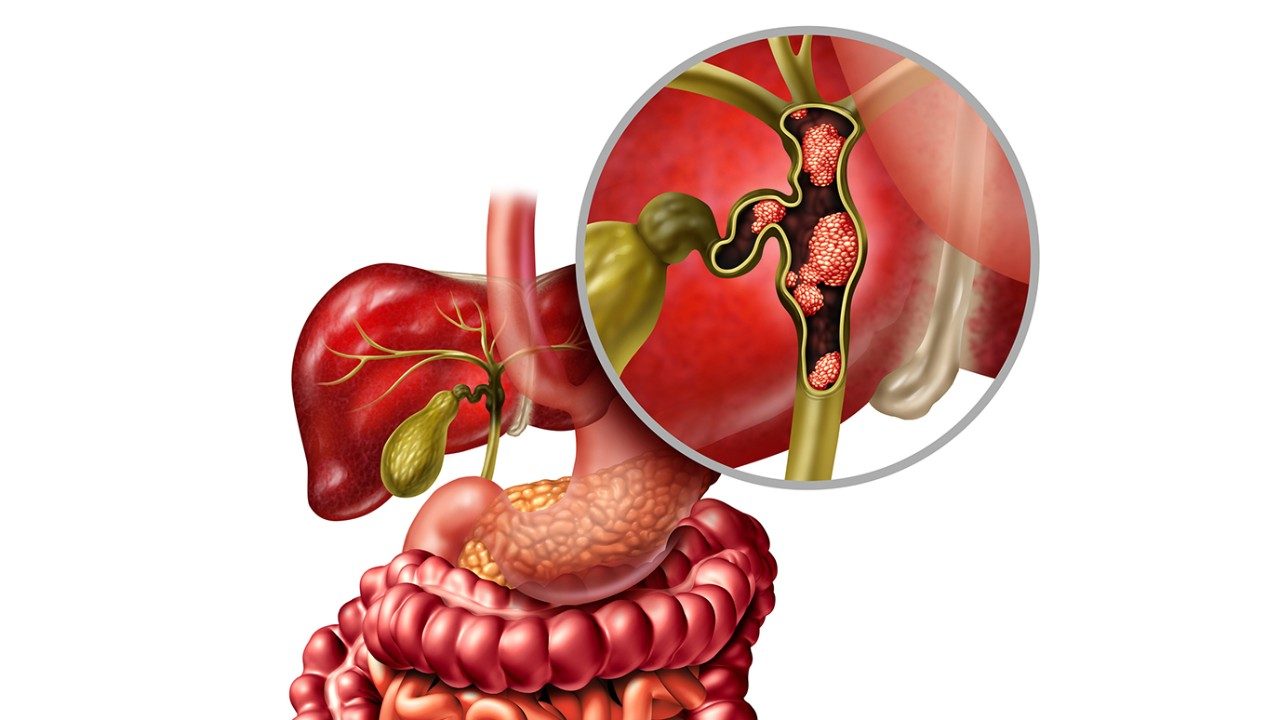
HER2-targeted therapy shows promising results in rare bile duct cancers
HER2-positive metastatic biliary tract cancer (BTC) is a rare and aggressive cancer with limited treatment options
Final results from the...
DNA shape and rigidity regulate key players of gene expression
Researchers found how the INO80 protein moves nucleosomes to specific positions that are important for gene regulation and DNA replication
INO80...
Researchers identify rare mutation that predicts strong immunotherapy response in colorectal cancer
A specific subset of POLE gene mutation, called loss-of-proofreading (LOP) mutations, makes colorectal tumors highly responsive to immunotherapy
Patients with the specific POLE mutations had long-lasting responses when treated with immunotherapy, whereas those with other POLE mutations did not see similar benefits
A new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center shows that a specific subset of mutations...
Study uncovers hidden class of BRCA1 mutations and a potential way to target them
HSP90 buffers certain BRCA1 mutations, allowing them to persist in humans and promote resistance to PARP inhibitor treatments
Low-dose HSP90...
Traces of bacteria inside brain tumors may affect tumor behavior
Researchers found bacterial genetic and cellular elements inside brain tumor cells that appear biologically active and may influence tumor...
MD Anderson experts spotlight key immunotherapy advances at 2025 SITC Annual Meeting
Major themes include strategies to reprogram the tumor microenvironment and prevent cancer before it starts
New insights from AI-based imaging...
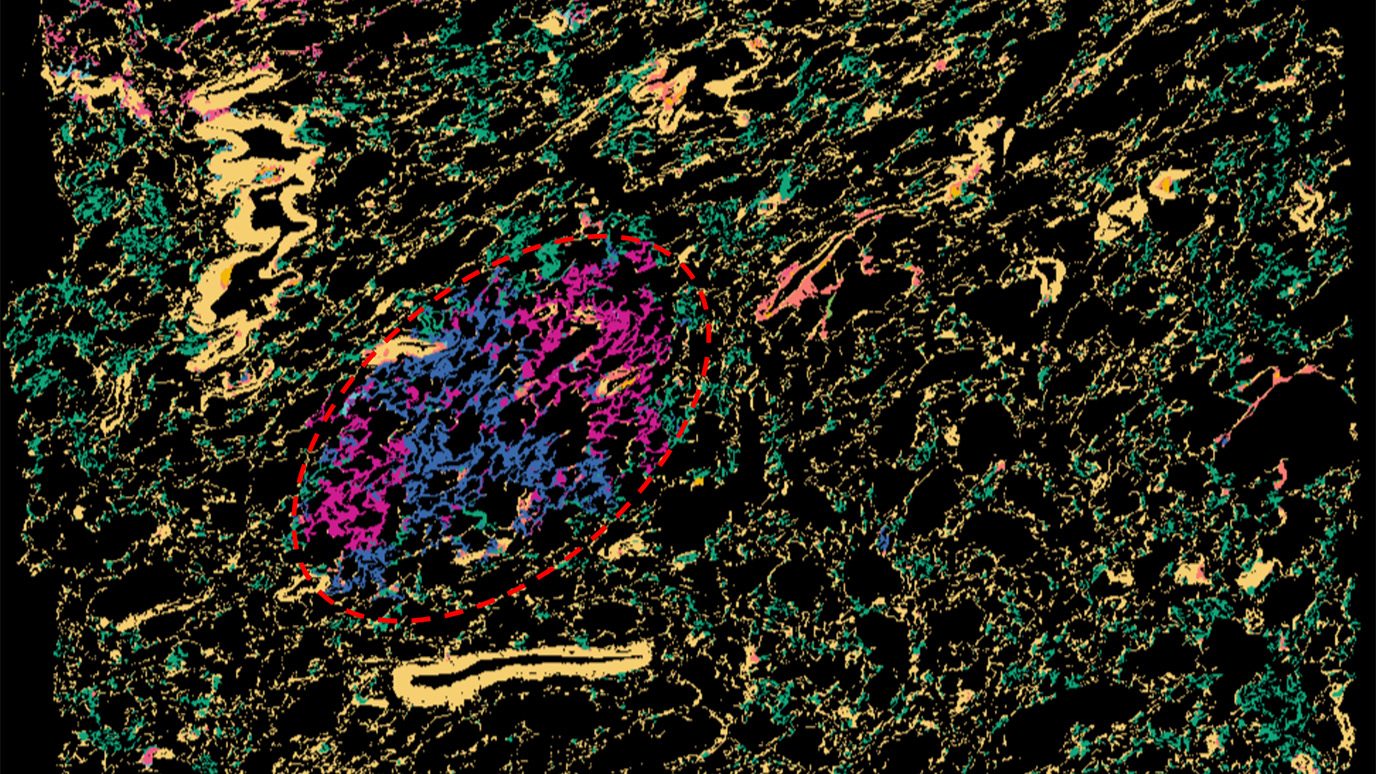
Inflammation may be responsible for driving earliest stages of lung cancer
Spatial maps of lung precancer and cancer cells at different points in development advance understanding of the earliest stages of lung cancer...
