Total neoadjuvant therapy: A new era for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer
When rectal cancer advances to involve nearby lymph nodes but hasn’t spread to other areas of the body, it’s considered to be locally advanced.
The traditional standard of care has been a three-part regimen consisting of chemoradiation followed by surgery and chemotherapy once again.
“The old approach has been turned on its head based on recent data,” says Josh Smith, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Colon and Rectal Surgery....

5 things to know about clonal hematopoiesis
Bone marrow is the factory for our blood cells. New cells are created as old cells divide and split. During that process, a mistake can sometimes...
Radiation therapy, the immune system and what’s ahead
Radiation therapy is often thought of as a treatment for localized cancer that hasn’t spread. But when paired with other therapies, it can...
Liver regeneration: How the liver’s ability to recover plays into liver cancer surgery
Did you know that the liver is the only internal organ that can regenerate? But it doesn’t grow back like a salamander’s tail. When a portion of the liver is removed, the remaining tissue grows bigger. This process is called hypertrophy.
We spoke with surgical oncologist Ching-Wei Tzeng, M.D., to learn what’s happening when a liver regenerates and what factors can impact success. He shared insights on the phenomenon, including...


Optimizing CAR T cell therapy with bridging radiation therapy
For many patients diagnosed with certain types of B-cell lymphoma, leukemia and multiple myeloma, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy...
Peripheral neuropathy: Causes, symptoms and treatments
Many patients receive chemotherapy as part of their cancer treatment plan. These drugs have long shown benefits in extending patients’ lives...
4 things to know about marginal zone lymphoma
Lymphoma is often thought of as a cancer of lymph nodes, but it's actually a cancer of the lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are white blood cells...
Antibody drug conjugates: A shift in treatment options for solid tumors
Antibody drug conjugates have existed for years, but several recent advances are helping to refine how these cancer drugs work, expanding...
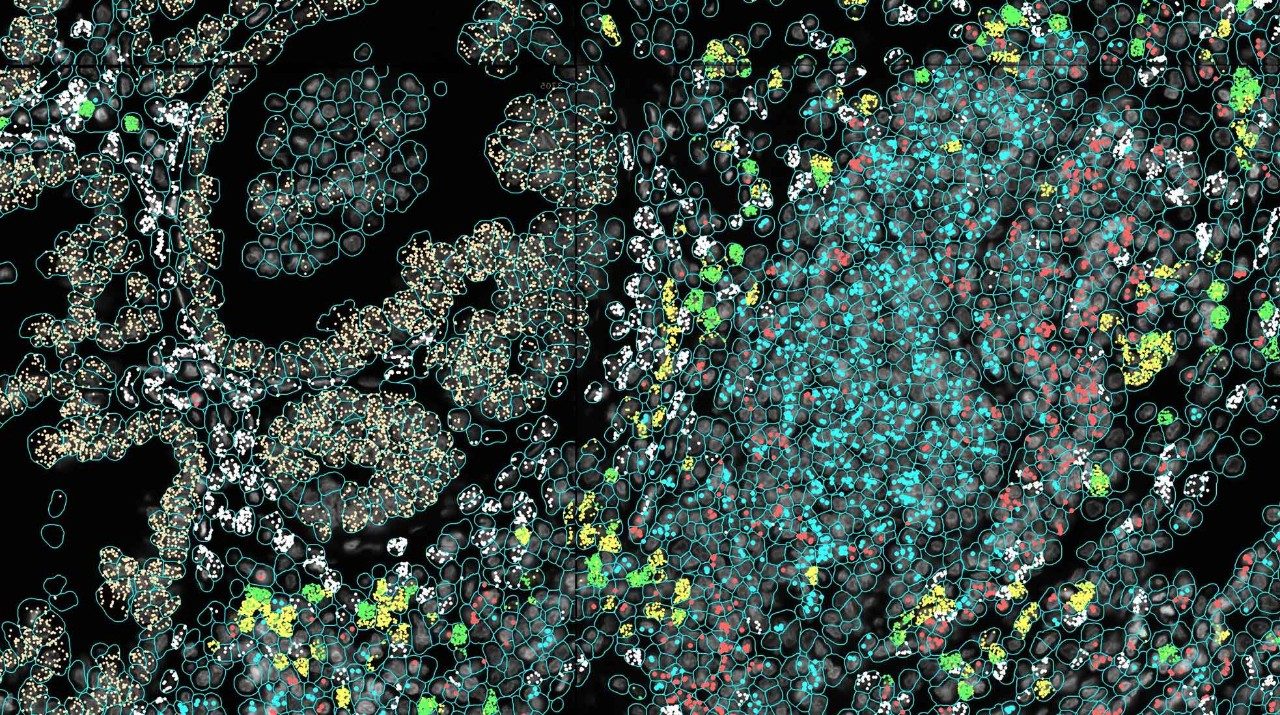
Spatial omics offer a deeper look at tertiary lymphoid structures in cancer
Tertiary lymphoid structures are highly organized clusters of immune cells that form in non-lymphoid tissues. They’re often found at sites...
How BTK inhibitors treat mantle cell lymphoma
B cells are an important part of the immune system. One of their jobs is to neutralize the threat from a foreign invader known as a pathogen...
